What Is Multi-Factor Authentication & When Should I Use It?
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission. Here’s how it works.
 If you’re not worried about your identity being stolen with your online activity, whether it’s making purchases on a website, online banking, or just being on social media, you should be. You could be at high risk for hackers and cyber thieves if you’re only using a password to access your accounts. It’s a sad state, but criminals have gotten smarter about getting past even complicated passwords.
If you’re not worried about your identity being stolen with your online activity, whether it’s making purchases on a website, online banking, or just being on social media, you should be. You could be at high risk for hackers and cyber thieves if you’re only using a password to access your accounts. It’s a sad state, but criminals have gotten smarter about getting past even complicated passwords.
Good news is there’s a better way to protect yourself that goes beyond a password — implementing multi-factor or two-factor authentication. We’ll give you all the information you need to know to understand why you need to enable this easy-to-use security technology, how to set it up, and where to find your best options.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication, or MFA, is an authentication method that requires users to provide two or more verification methods to gain access to an application, online account, a VPN (virtual private network), or other types of online activity.
Instead of simply using your username and password, MFA security requires you to provide additional credentials. This decreases your risk of falling prey to cybercrime.
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
You may have also heard the term two-factor authentication, also called 2FA. While technically different from multi-factor authentication for tech geeks, the two terms are often used interchangeably these days. Essentially 2FA involves using two factors to gain access, while multi-factor authentication can involve two or more factors.
For example, Microsoft Office 365 calls their authentication multi-factor, but it only requires using your password and one other authentication method (a dynamically generated verification code provided by an authenticator app or sent to your phone). And the popular LastPass Authenticator app works the same way.
For this article, we’ll be using the terms interchangeably.
 Benefits Of Multi-Factor Authentication
Benefits Of Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA security’s primary benefit is to add additional security layers to reduce the risk of a variety of cyber attacks for individuals and businesses. Data breaches are costly for any business. In fact, a recent report by IBM found that the average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million.
And for individuals, you’re at risk of having your identity stolen or being a victim of credit card fraud if all you’re using is a simple password when you’re online.
Types And Examples Of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication typically requires two or more of the following authentication methods:
1. Something You Know (Knowledge)
Knowledge factors are the most common type of security, but they’re also the most vulnerable. They’re less secure because the information is easier to share or steal. Examples of something users know include:
- Passwords (find the best password manager)
- PINs (personal identification numbers)
- Answers to security questions, e.g., “Where were you born?” or “What was your first pet’s name?”
2. Something You Have (Possession)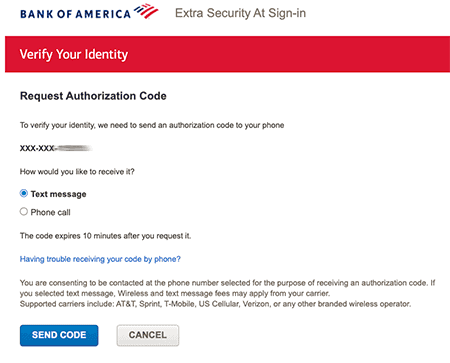
Think of this factor as a physical key that opens a lock. Of course, in today’s technology, possessions are far more complex than a basic key, but the idea is the same.
Essentially, it’s a trusted physical device that’s not easily duplicated. Examples include:
- Smartphone (one-time passcodes sent via an authenticator app or through an SMS text message)
- USB devices
- Software or hardware tokens
- Security keys
- Access badges
3. Something You Are (Inherence)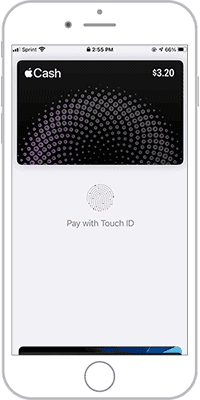
This factor involves a biometric verification to identify you from your unique biological traits. Examples include:
- Fingerprints
- Facial recognition
- Retina or iris scanning
- Voice recognition
How To Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
You have several options on how you can set up two-factor authentication (also often called two-step verification) for a safer online experience.
Authenticator Apps
 Authenticator apps are easy to use, are generally considered a secure way to set up two-factor authentication, and don’t require an internet connection.
Authenticator apps are easy to use, are generally considered a secure way to set up two-factor authentication, and don’t require an internet connection.
Each of these apps displays a randomly generated six-digit code that refreshes every 30 seconds or so. You simply enter the code into whichever account (websites, social media, services, etc.) you’re logging into.
With each new account you add, you scan a QR code associated with that account (or type in a code), and it’s automatically saved in the app. The next time you log in to your account, it will ask for the required code, so all you have to do is open the authenticator app to find the code.
Here’s a quick list of some of the most popular authenticator apps, but there are a lot to choose from for your iOS or Android devices.
- Google Authenticator (Android | iOS)
- Twilio Authy (Android | iOS)
- Microsoft Authenticator (Android | iOS)
- LastPass Authenticator (Android | iOS)
Text Messaging
Many websites and services that support 2FA offer you the option of sending you a one-time numeric code to your phone via SMS texting, and then you simply enter that code when logging into the site. However, keep in mind that texting isn’t considered as secure as using an authenticator app because text message authentication is easier to hack.
Some experts are warning against using SMS texting for authentication verification. According to a recent Microsoft article, the director of identity security at Microsoft, Alex Weinert, believes that SMS is the least secure method of using authentication these days.
Hardware Security Key

These hardware keys are based on the FIDO U2F security protocol standard, which is extremely difficult for hackers to intercept.
Yubico security company (which helped develop the standards along with Google) offers different keys for devices with USB-A, USB-C, or NFC ports, and they work with a wide variety of apps. You can also opt for this Thetis FIDO2 fingerprint security key, which plugs into your USB-A port for multi-layered security.
 Which Providers Offer 2FA?
Which Providers Offer 2FA?
The good news is that a growing list of companies now support 2FA to help their customers stay more secure with their online accounts. The easiest way to find out if 2FA or MFA is supported is to login to your account and visit your profile or account settings page, security or login settings, and see if 2FA or MFA is offered. If not, or if you can’t find the setting, contact your provider and ask them how to enable 2FA.
Here’s a list of some popular sites that support 2FA.
- Amazon
- Apple
- Dropbox
- Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Snapchat, Twitter
- Gmail
- Microsoft
- Paypal
MFA & 2FA Software For Businesses
Many businesses also use two-factor or multi-factor authentication as a required security measure for their employees. This can help companies prevent data breaches, as well as external access from competitors or unwanted parties. Some popular business solutions include:
How To Turn Off Two-Factor Authentication On iOS (iPhone)
 Our readers ask us this question a lot: How do I turn off two-factor authentication on my iPhone? In some cases, you may not be able to. Apple removed the ability to turn off two-factor authentication on some Apple IDs created in iOS 10.3 (or macOS 10.12.4) and later.
Our readers ask us this question a lot: How do I turn off two-factor authentication on my iPhone? In some cases, you may not be able to. Apple removed the ability to turn off two-factor authentication on some Apple IDs created in iOS 10.3 (or macOS 10.12.4) and later.
However, if you recently updated your account, you can disable it within two weeks of enrollment. Just open your enrollment confirmation email and click the link to return to your previous security settings.
If you created your Apple ID in an earlier version of iOS, you could turn off two-factor authentication. To turn it off:
- Go to appleid.apple.com
- Enter your username and password — they’ll send an authentication code to your iPhone; then enter that code
- Go to the “Security” section and click “Edit”
- Click “Turn Off Two-Factor Authentication” (if you don’t see this, you can’t turn it off)
How Else Can I Protect Myself From Identity Theft?
Using multi-factor authentication when you’re online is only one way you can protect yourself from identity theft. Are you monitoring your credit reports? Are your devices protected with firewalls? What other steps can you take to stay safe? Read our ultimate guide to identity theft to learn about everything you should be doing to be secure.



