Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Real? How Are They Made?
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission. Here’s how it works.

You might scoff at the idea of lab-grown vs natural diamonds. While lab-created diamonds are a booming industry these days for many reasons, you’re probably wondering, are man-made diamonds real? Contrary to what you might think, they indeed are considered real diamonds by gem experts.
Still, you likely want to know how they differ from naturally mined diamonds and if they’re a sound purchase or investment as an alternative to natural diamonds. We’ve unearthed all the details you need to know to help you decide if a lab-grown diamond is your best option for an engagement ring or other jewelry.
What Is A Lab-Grown Diamond?
Laboratory-grown diamonds, also known as manufactured, cultured, or synthetic diamonds, are grown in laboratories using advanced technology that duplicates how diamonds naturally develop in the earth’s mantle. According to the American Gemological Institute (AGI), lab-grown diamonds exhibit the same optical, physical, and chemical properties and crystal structure as natural diamonds.
The International Gem Society (IGS) adds that lab-grown diamonds also have the same brilliance and sparkle as natural diamonds as well as the Mohs hardness of 10, meaning they’re just as durable. The multiple similarities, plus the lower cost, are why man-made diamonds are so popular.
How Are Diamonds Made In A Lab?
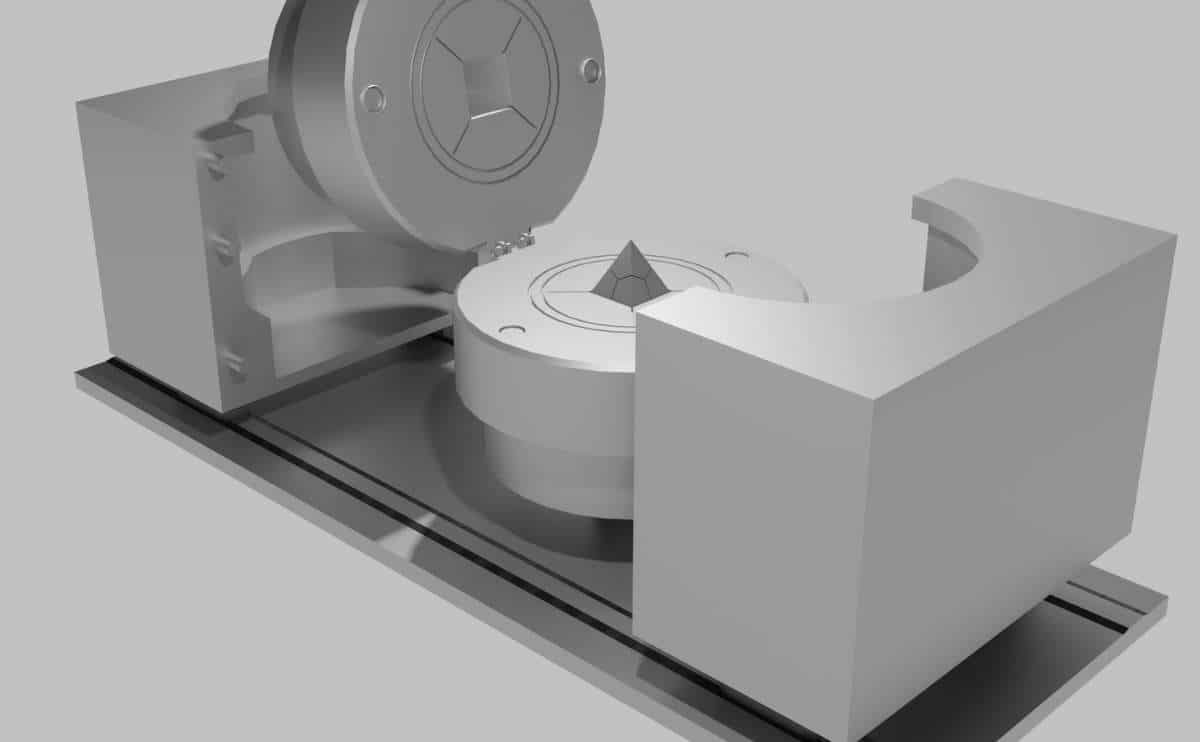
Scientists use advanced technology to mimic how natural diamonds form, implementing one of two methods — Chemical Vapor Deposition or High Pressure High Temperature. Lab diamonds take six to 10 weeks to form. Then, the rough diamond is cut, polished, and placed in a setting.
Chemical Vapor Deposition
With Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), scientists place a tiny diamond seed, often called a seed crystal, in a small chamber. They add a mixture of hydrogen and carbon-containing gases and heat the chamber. Once the gases reach a high enough temperature, layers of crystallized carbon begin to form on the seed crystal. This causes the seed to grow, resulting in a square-shaped diamond crystal.
High Pressure High Temperature
The second technology, High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT), mimics the natural method under which diamonds form inside the earth. In this process, scientists place a diamond seed into a carbon source, such as graphite, in a machine that exerts extreme pressure and heat. As the pure carbon melts, a diamond forms around the seed crystal. This method, which was created back in the 1950s, is more costly and requires more energy than CVD.
To create lab-grown colored diamonds using CVD and HPHT, scientists introduce small amounts of specific trace elements during the growth phase of the diamond (just as it occurs in nature). In both white and fancy-colored lab diamonds, the exact composition of these trace elements can differ from natural diamonds.
Should I Buy A Lab-Grown Diamond?
One of the first questions people ask is: are lab-created diamonds worth anything? Yes, lab diamonds are an excellent value, particularly if you’re on a tight budget. Manufactured diamonds are graded on the same scale as earth-mined diamonds using the 4Cs of diamond quality – cut, color, carat, and clarity. The only main difference is their point of origin.
There are several benefits of lab-grown diamonds, but some people may find drawbacks. Consider these pros and cons.
Pros
Environmental Sustainability
Mining destroys the Earth’s crust and mantle. It also takes considerably less energy to grow a diamond in a lab than it does to mine one out of the ground. Finally, there are limited resources on the earth, and this includes diamonds. Thus, this rare natural gem is likely to increase in price as supplies dwindle, making lab-created diamonds a more sustainable choice.
No Risk Of Ethically Compromised Diamonds
The diamond mining industry has a history of unfavorable practices, including human rights violations, child labor, and poor working conditions. Also, the issue of conflict or “blood” diamonds is a significant factor in many consumers’ minds. Blood diamonds are sold to pay for bloody wars involving anti-government militias that kill thousands. With a lab-grown diamond bought from a reputable source, you can be confident that your purchase isn’t supporting wars or child labor.
Price
You can save 30-40% or more with a manufactured diamond over a natural one. The savings can be even higher if you want a colored diamond — earth-mined colored diamonds are incredibly scarce and consequently very expensive.
Cons
Negative Economic Impact On Developing Areas
While lab diamonds support advanced economies, they also take jobs away from impoverished areas around the world that depend on the jobs and income from diamond mines.
One-Of-A-Kind Factor
Every mined diamond is a unique creation of nature. Synthetic diamonds, however, are mass-produced in labs. Some people may find that the glamour, mystery, and romance of the precious gemstone are lost with lab diamonds.
Lab-Grown Diamonds vs Moissanite vs Cubic Zirconia
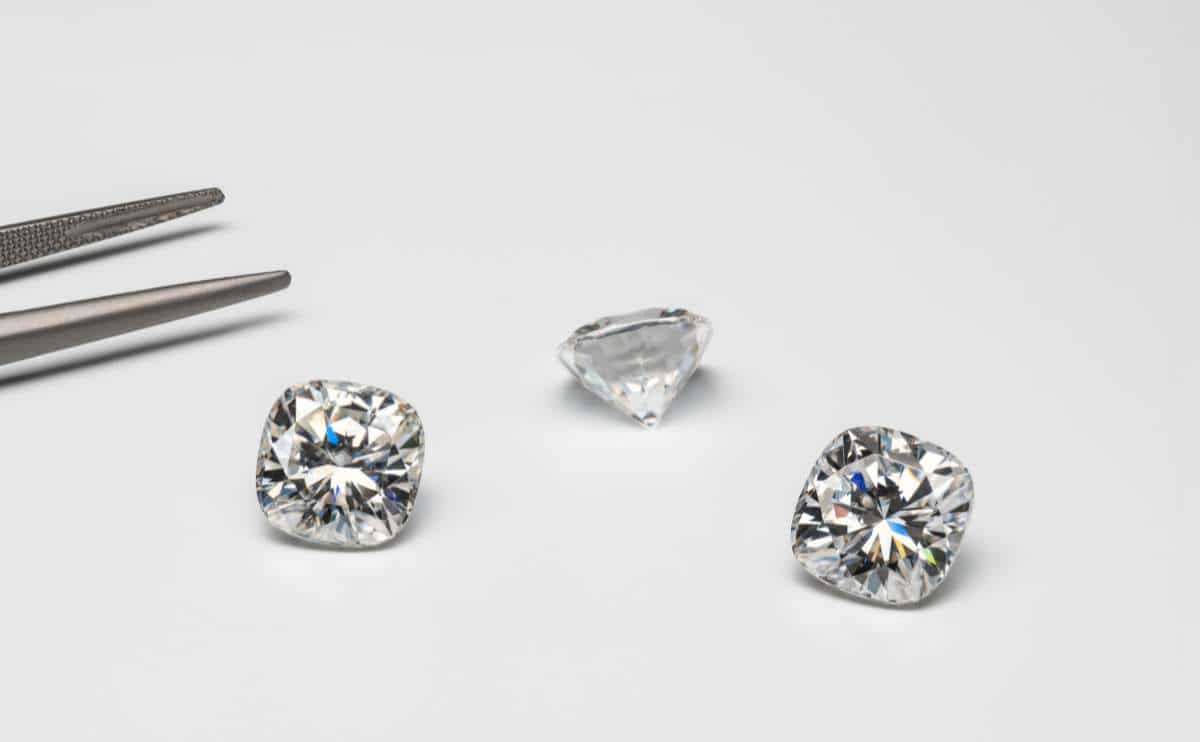

We’ll break down the differences between the most popular alternatives. Lab diamonds are created from carbon, so they’re technically real diamonds.
The popular gems moissanite and cubic zirconia look similar to diamonds but are not created with carbon crystals; therefore, they’re called diamond simulants. Unlike real and lab-grown diamonds, moissanite and cubic zirconia are considered non-precious gems.
Moissanite vs Diamonds
Moissanite does occur naturally, but it’s extremely rare (it’s only found in meteorites). So, the moissanite you find in jewelry stores is lab-created. It consists of silicon carbide rather than carbon, so it’s an entirely different gemstone.
From a distance, Moissanite might appear somewhat similar to a diamond, but the two are noticeably distinct upon closer inspection — even to a non-expert’s eye. Moissanite isn’t nearly as clear and brilliant as a diamond. It’s also not quite as durable as a diamond, with a 9.5 hardness on the Mohs scale. Although you can save 50-75% of what you’d pay for a diamond, you’re not getting a valuable, precious gemstone.
Cubic Zirconia vs Diamonds
Entirely man-made, cubic zirconia (CZ) is another popular diamond simulant, but it’s not as durable as moissanite. With an 8.5 on the Mohs hardness scale, it can scratch and show wear and tear over time because it’s not as hard. CZ is also less brilliant and sparkly than diamonds and moissanite. It’s considered a third-tier option, but it’s more affordable than moissanite.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some questions our readers often ask about lab-grown diamonds and diamond alternatives. Don’t see yours here? Hit us up in our comments section.
Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Tacky?
Just a few years ago, many consumers considered man-made diamonds cheap or tacky. However, attitudes are rapidly shifting. According to the IGS, nearly ⅔ of people aged 21-40 are now willing to consider lab-grown diamonds when shopping for an engagement ring.
Are Man-Made Diamonds A Good Investment?
Generally, mined diamonds are considered a good investment because they retain and can even gain in value. Lab-created diamonds aren’t as scarce as natural diamonds, so they’re not as wise of an investment. Their resale value is relatively low compared to mined diamonds, and they may not retain their value over time as much as natural diamonds.
Can A Diamond Tester Tell The Difference?
Most diamond testers can’t detect a man-made diamond because they have the same thermal and electrical conductivity as mined diamonds. The only way to distinguish between lab-grown vs natural diamonds is by using highly specialized equipment that can detect minor differences in crystal growth and trace elements. See a demonstration in this brief video.
Where Can I Buy Lab-Grown Diamonds?
Many jewelry stores carry manufactured diamonds these days, but you can also find lab-grown diamond engagement rings and other jewelry online through trusted online retailers like James Allen.
Looking For An Engagement Ring Or Wedding Bands?
First, read our discussion on the differences between engagement and wedding rings if you need some clarification on what to look for. And be sure to check out our guide on when to buy an engagement ring. If you’re a gay couple, see our articles on gay men’s engagement rings and lesbian engagement rings. Finally, if you’re on a tight budget, you may want to consider an alternative metal, like titanium. Learn more about this affordable option in our reviews of the best titanium rings.
Why Trust Safe Smart Living?
Sally has extensive professional scientific/technical research and writing experience, covering everything from diamonds and DNA to smart home gadgets and home security. She’s also Safe Smart Living’s resident expert on financial planning. For over eight years, Sally’s been part of the trusted Safe Smart Living team of experts who aim to make your life smarter, safer, and more enjoyable.



